Domain Driven Data Mining (DDDM, D3M), or Domain-Driven Actionable Knowledge Discovery
(AKD), aims for next-generation data mining/analytics/science methodologies, techniques
and real-life enterprise applications by involving and synthesizing
ubiquitous data, information, resources and intelligence in data mining/analytics/science
problems and environment as per domain-specific conditions and requirements, and delivering actionable knowledge and actionable intelligence
that satisfies both technical significance and business needs and
support operations, policy and decision-making actions for business and impact.
DDDM-AKD Aims
-
to design next-generation data mining/analytics methodologies for actionable knowledge discovery and delivery, toward handling critical issues in data mining, knowledge discovery and advanced analytics to effectively and efficiently contribute to real-world smart businesses and smart decision and benefit critical domain problem-solving in theory and practice;
-
to devise domain-driven actionable knowledge discovery techniques and algorithms to bridge the gap between a business-to-theory-converted problem and its actual business problem, between academic objectives and business goals, between technical significance and business interest, and between discovered knowledge and business expected deliverables, toward strengthening business intelligence and impact in complex enterprise applications;
-
to present the applications of domain-driven actionable knowledge discovery and demonstrate how data analytics can be effectively deployed to solve complex practical problems; and
-
to identify challenges and future directions for data mining, knowledge discovery, AI and data science research and applications in the dialogue between academia and industry.
DDDM-AKD Concept Map
The following figure shows the concept map of DDDM.
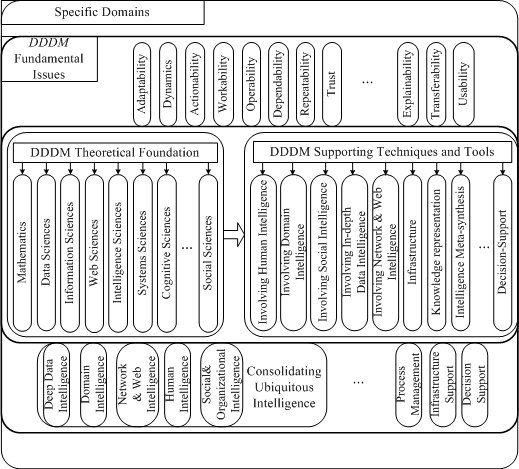
Figure 1. The concept map of DDDM-AKD [1-3].
- [1] Longbing Cao, Philip S Yu, Chengqi Zhang and Yanchang Zhao. Domain Driven Data Mining, ISBN: 978-1-4419-5737-5, Springer, 2010
- [2] Longbing Cao. Actionable Knowledge Discovery and Delivery, WIREs Data Mining and Knowledge Discovery, 2(2): 149-163, 2012
- [3] Longbing Cao. Domain Driven Data Mining: Challenges and Prospects, IEEE Trans. on Knowledge and Data Engineering, vol. 22, no. 6, pp. 755-769, 2010.